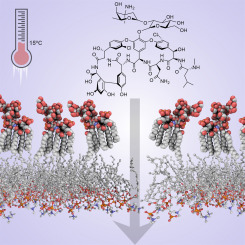
Abstract:
A poor understanding of the mechanisms by which antibiotics traverse the outer membrane remains a considerable obstacle to the development of novel Gram-negative antibiotics. Herein, we demonstrate that the Gram-negative bacterium Escherichia coli becomes susceptible to the narrow-spectrum antibiotic vancomycin during growth at low temperatures. Heterologous expression of an Enterococcus vanHBX vancomycin resistance cluster in E. coli confirmed that the mechanism of action was through inhibition of peptidoglycan biosynthesis. To understand the nature of vancomycin permeability, we screened for strains of E. coli that displayed resistance to vancomycin at low temperature. Surprisingly, we observed that mutations in outer membrane biosynthesis suppressed vancomycin activity. Subsequent chemical analysis of lipopolysaccharide from vancomycin-sensitive and -resistant strains confirmed that suppression was correlated with truncations in the core oligosaccharide of lipopolysaccharide. These unexpected observations challenge the current understanding of outer membrane permeability, and provide new chemical insights into the susceptibility of E. coli to glycopeptide antibiotics.
Authors:
Stokes JM, French S, Ovchinnikova OG, Bouwman C, Whitfield C, Brown ED.
Reference:
Cell Chem Biol. 2016 Feb 18;23(2):267-77